India's contribution in mitigating carbon Emission comparative to other countries
Climate Change
Climate change refers to the change of climate directly or indirectly because of human activities that alter the composition of the global atmosphere. It refers to changes in climate characteristics, including temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind, and harsh weather events over long-term periods.
Causes of Climate change
As we know there are many reasons due to which the world is experiencing climate change, some of them are:
When fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas are burnt, they release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, because of this the layer of greenhouse gas is getting thicker which is, in turn, making the earth warmer. Similarly, there are other gases like methane, chlorofluorocarbons, and nitrous oxide, emitted through different human activities like industrial fume, vehicles, stubble burning, fire in the forests, etc. which contributes to the process of climate change.
Climate change in India
India is not historically responsible for climate change, but still, India and other developing nations are doing more than the developed countries to reduce carbon emissions. The latest Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI) 2021 has placed India among the top 10 countries to have adopted considerable measures to mitigate climate change. This is for the second consecutive year Indi has been Placed in the top 10 countries.
India is the 13th most vulnerable country to climate change. Since more than 60 percent of its agriculture is rainfed and it hosts 33 percent of the world's poor, climate change will have significant impacts on food and nutritional security. According to a study by the Council on Energy, Environment, and Water (CEEW), about three in four of India's districts are hotspots of extreme climate events such as cyclones, floods, droughts, heat, and cold waves. Here is a series of maps that capture climate change impacts on the country
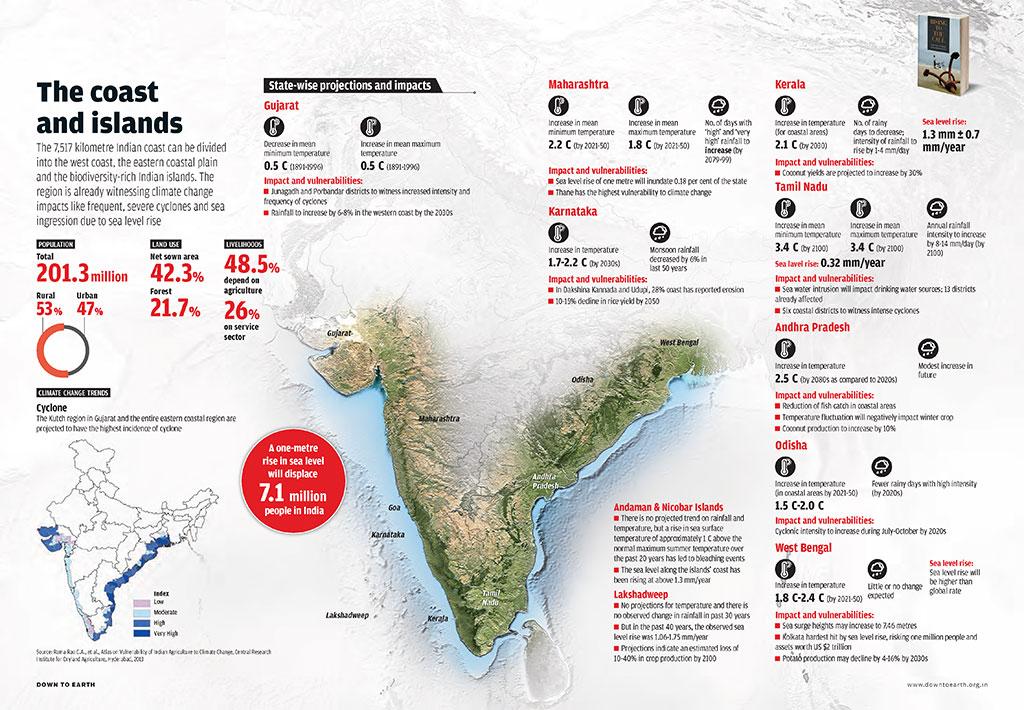
India is already the fifth most vulnerable country globally in terms of extreme climate events and it is all set to become the world’s flood capital.

Comparing India and Other Nations: Equity is Key to Stopping Climate Change
Issues such as increasing historical emissions are slowly being phased out of the climate change discourse, by that the responsibility of a handful of countries like the United States, the United Kingdom, the European Union, Japan, Russia, Canada, and Australia, for creating the problem of global warming has been removed, as many other countries also joined this trend of emissions for the sake of their technological and economic advancement so that they can also participate in the race of developed countries and short their status from developing nation to developed nation.
Since 2001, China has also become part of the problem. Together, the seven rich countries, along with China, will control over 70 percent of the carbon space left between 2020 and 2030.

As in the race of this developed and developing nation, developed nations are already contributing in the emission since 1870, whereas developing nations had joined in the past decade but still the unjust share of carbon emissions that have helped a certain group of countries develop while putting pressure on poor countries that are still developing to take unjust mitigation measures. This inequitable distribution of carbon emission and equal steps for mitigation, will net zero emissions targets by 2050 help mitigate climate change?
Here is some data which show this unequal participation in the emission and equal participation in the mitigation process by India and other developing nations comparative to developed nations:


China, the world’s most populous country now generates a major part of Earth’s pollutants. This, however, was not the case always. Historically — from 1870 to 1989 — these were the biggest polluters:
- The United Kingdom
- The United States
- Russia
- Japan
- Australia
- Canada
- The European Union
Together, they emitted 77 percent of the world’s carbon dioxide (CO2). The US alone emitted 31.26 percent. At that time — three years before the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) was drafted — China emitted only 5.11 percent. But between 1990 and 2019 its quadrupled to 20.7 percent.

India is the third-largest polluter after China and US but there is a large difference between the emission of India and the other two Largest emitters, i.e. 10.17 gigatonnes by china, 5.28 gigatonnes by the USA, and 2.62 gigatonnes by India.
At the current rate, the world will exhaust the remaining carbon budget. Developing countries and poor countries like Chille ( whose per capita emission is 4 tonne), Zambia, Botswana, are ready to take the greatest share of emission reduction, their per capita reduction is already low but they are ready to reduce further in the interest of keeping world safe, they are taking the bigger burden to reduce emission, they are saying they will get technology and money as promised twelve years ago, at United Nations Climate Summit in Copenhagen to channel US$ 100 billion to less wealthy nations by 2020; So, at the same time developed and wealthy countries must come forward and shouldn't ignore the principle of equity and reduce their emission in proportion to their past emission and help least develop and poor countries so that they can grow economically and support the world in saving the environment.
Major Initiatives are taken by the Indian Government to combat climate change:
It was in 2015 when nations across the globe met in Paris, and 197 signatory countries have promised to own up and to limit the increase to no more than 1.5 degrees over the pre-industrial levels by 2030. India is one of them. India has promised to cut its emission intensity by 33-35% by the year 2030, as compared to 2015 levels. It looks like this is desirable and achievable. Some other initiatives are:
- International Solar Alliance
- National Action Plan on Climte change- The Government of India launched National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) on 30thJune, 2008 outlining eight National Missions on climate change. These include:
- National Solar Mission
- National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency
- National Mission on Sustainable Habitat
- National Water Mission
- National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Eco-system
- National Mission for a Green India
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture
- National Mission on Strategic Knowledge for Climate Change
The Department of Science & Technology, Ministry of Science & Technology was entrusted with the responsibility of coordinating two out of these eight national missions on climate change. These are:
- National Mission for Sustaining Himalayan Ecosystem (NMSHE) and
- National Mission on Strategic Knowledge for Climate Change (NMSKCC).
- International Solar Alliance
- FAME Scheme for E- mobility
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation & Urban Transformation (AMRUT) for smart cities
- Pradhan Mantri Ujawala Yojana
- Ujala Scheme
Way Forward
- India has technology but need to work on Research and Development to reach our targets.
- The real challenge is to get other developed countries on board, to move shoulder to shoulder in mitigating carbon emission as they are the major emitter since industralisation. Developed Countries should avoid diluting the CBDR principle anticipated in earlier agreements.
- Replacing and banning single use plastic will also act as a game changer
- India should treat climate change as developmental challenge instead of treating it as environmental change.
- Investment in R&D is needed to stimulate innovations in sustainable climate-friendly productivity, and the private sector can help on this.
- India’s ambitious targets to cut carbon emissions by 33-35% by the year 2030, as compared to 2015 levels require sustainable plans.
- Climate finance can prove to be a compelling financial tool to align India’s growth with various climate change measures.
At the end I would like to quote :
If we take climate action seriously, this means that we must not only take action in our own country but must also, and in particular, significantly scale up our efforts for global climate protection. Because saving the climate is vital to the survival of humanity.
Dr. Gerd Muller (Federal Minister for Economic Cooperation and Development )
Source: The Hindu, downtoearth.org.in, dst.gov.in, Ourworldindata.org